
When considering the foundation of a building, the choice often becomes the defining factor for the structure’s longevity and performance. One such foundation type that has garnered attention for its simplicity and efficiency is the Slab-on-Grade foundation. This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of this foundation type, its construction process, benefits, and potential drawbacks.
What is a Slab-on-Grade Foundation?
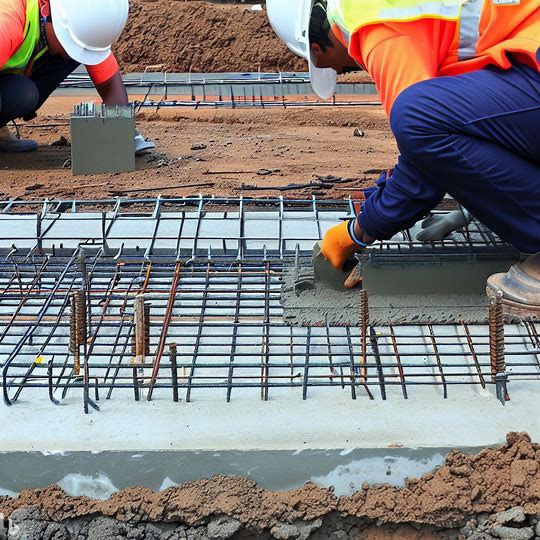
A Slab-on-Grade foundation is a type of concrete foundation that is poured directly onto the ground. It is a popular foundation choice for homes and other structures in areas with warm climates that do not experience significant frost heave.
Slab-on-grade foundations are typically made of reinforced concrete that is 4-6 inches thick. The concrete is poured into a mold that has been set on the ground and leveled. The mold is then removed, and the foundation is allowed to cure.
Slab-on-grade foundations can be either monolithic or post-tensioned. Monolithic slabs are poured in one continuous piece, while post-tensioned slabs have steel cables that are tensioned after the concrete has cured.
Key Components of Slab-on-Grade Foundations
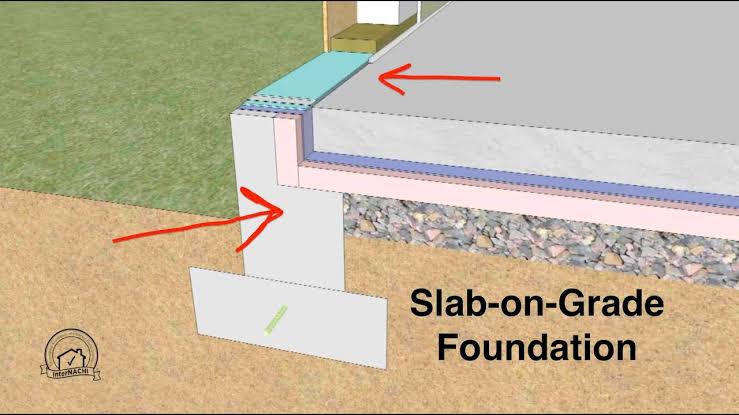
Slab-on-grade foundations are made up of three key components: the slab, the reinforcement, and the edge thickening or grade beams.
- The slab is the main horizontal layer of concrete that supports the structure. It is typically 4-6 inches thick and reinforced with steel bars or mesh to increase its strength.
- The reinforcement is the steel bars or mesh that are embedded in the concrete slab to provide tensile strength. The reinforcement helps to prevent the slab from cracking under stress.
- The edge thickening or grade beams are thicker sections of concrete that are placed around the perimeter of the slab. They provide additional support for the slab and help to distribute the weight of the structure more evenly.
Benefits of Slab-on-Grade Foundations
Slab-on-grade foundations offer several benefits, including:
- Cost-effectiveness: Slab-on-grade foundations are one of the most affordable foundation types. They require fewer materials and less labor than other foundation types, such as basements or crawl spaces.
- Speedy construction: Slab-on-grade foundations can be constructed quickly, which can save time and money. There is no need to excavate deep into the ground, which can significantly shorten the construction timeline.
- Low maintenance: Slab-on-grade foundations are relatively low maintenance. There is less potential for problems such as basement leaks, which can lead to reduced maintenance costs.
- • Energy efficiency: Slab-on-grade foundations can be energy-efficient, especially when the slab is properly insulated. The absence of a crawl space or basement can help to reduce heat loss in the winter and heat gain in the summer.
Potential Limitations of Slab-on-Grade Foundations
Slab-on-grade foundations offer several benefits, but they also have some potential limitations. These limitations include:
- Lack of basements: Slab-on-grade foundations do not have basements, which can reduce storage space or living area potential. If you need additional space, you may need to build an addition or consider a different foundation type.
- Ground movement concerns: In areas with expansive clay soils, the slab on the grade foundation may be prone to shifting, which can cause structural issues. It is important to have the soil tested before building to determine if it is suitable for a slab-on-grade foundation.
- Water drainage: The surrounding land must be graded properly to prevent water from pooling around the structure. This can help to prevent the foundation from becoming waterlogged and damaged.
- Potential for cracking: Like all concrete structures, there is a risk of cracking over time, especially if there is significant ground movement. If the slab cracks, it can allow water and moisture to seep in, which can damage the foundation and the home.
Considerations for Optimal Slab-on-Grade Construction
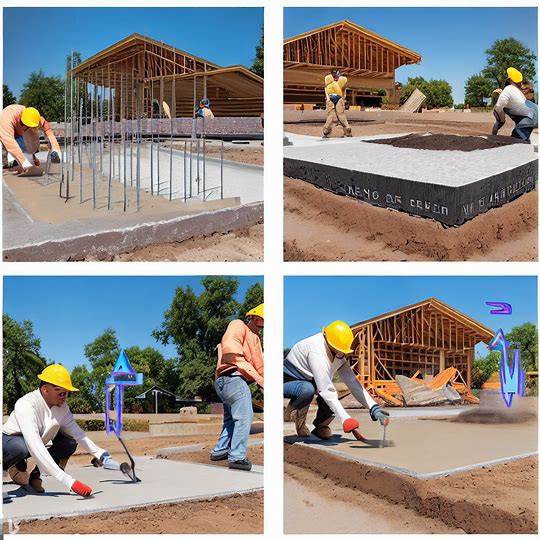

To ensure the longevity and structural integrity of a Slab-on-Grade foundation, it is important to take into account several factors during construction. These factors include:
- Soil quality: A thorough soil test should be conducted before construction to ensure that the ground can adequately support the weight of the slab and the structure that will be built on top of it.
- Proper insulation: In colder climates, it is important to insulate the slab to prevent cold bridges and ensure energy efficiency. This can be done by using a layer of insulation between the slab and the ground, or by installing a radiant heating system.
- Reinforcement placement: Proper placement of reinforcement can significantly reduce the risk of cracking and improve the slab’s lifespan. Reinforcement is typically made of steel bars or mesh that are embedded in the concrete slab.
The Slab-on-Grade foundation offers a compelling blend of cost-effectiveness, speed, and efficiency, making it an appealing choice for many construction projects. However, like all foundation types, it comes with its own set of considerations and potential challenges. By thoroughly understanding these aspects and working with experienced professionals, you can ensure that your Slab-on-Grade foundation serves your structure well for years to come.







Leave a comment